Abstract
Are you good at tossing a Frisbee®? It is great when you throw a perfect, arcing curve, right on target! If you can do that, you have already trained your arm on the aerodynamics of Frisbee flight. Why not treat your brain to some Frisbee science with this project?Summary
- Frisbee® is a registered trademark of Wham-o Inc.

Objective
Use aerodynamic principles to predict the flight distance for a Frisbee.Introduction
Tossing a Frisbee with your friends is a great way to have fun in the sun. As you practice your throws and become more accurate, you are learning about the aerodynamics of Frisbee flight intuitively. You are learning the body mechanics that will make the Frisbee go where you want it to go. This science project will get the thinking part of you into your Frisbee tossing. Who knows, it might even help you get better!
 Image Credit: Louis Desroches
Image Credit: Louis Desroches
Figure 1. Tossing a Frisbee with friends can be a lot of fun, and can be a great way to learn more about aerodynamics! (Louis Desroches)
Two key forces that act on a Frisbee during its flight are lift and drag. Lift is the force that allows a Frisbee to stay in the air, and it opposes the force of gravity on the mass of the Frisbee in flight. The Frisbee itself creates this lift force as it flies through the air. As the frisbee flies along, it deflects some air downward. Since every action must generate an equal and opposite reaction (Newton's third law of motion), this means that the air pushes back up on the frisbee, generating lift. Drag is a backward force on the Frisbee, and it goes against the Frisbee's movement through the air. The force of drag acts perpendicular to the force of lift. Figure 2 below shows how lift and drag act on a Frisbee. The NASA websites listed in the Bibliography are a great place to start learning more about the concepts of lift and drag, including explanations of some common misconceptions about how lift is generated.
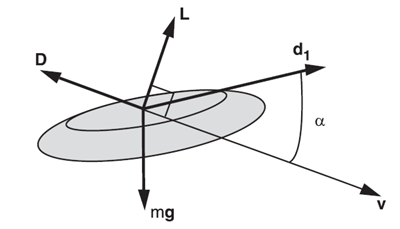 Image Credit: M. Hubbard and S.A. Hummel / Copyrighted
Image Credit: M. Hubbard and S.A. Hummel / CopyrightedThe initial throw of a frisbee gives the frisbee energy to fly in the direction it is thrown. Air that surrounds the frisbee provides lift that pushes it upward. Air resistence pulls on the frisbee in the opposite direction that it is traveling as drag. Finally gravity will constantly pull the frisbee towards the center of the Earth. A frisbee can only stay in the air for as long as the forces of lift and thrust are stronger than thes force of drag and gravity.
Figure 2. This diagram shows the forces on a Frisbee in flight. The arrow v shows the direction of flight (v stands for velocity). The downward arrow mg is the weight of the Frisbee (mass times gravity). The backward arrow, D, is the force of drag. The upward arrow L is the force of lift. It acts perpendicular to the direction of flight and drag. Both lift and drag change as a function of the angle of attack, α, of the disc, shown here as the difference between the direction of flight (v) and the direction the Frisbee is pointing (d1). (Hubbard and Hummel, 2000)
You will notice in the diagram above that the Frisbee can travel at an angle. This can be caused by throwing the Frisbee at an angle. That is, at the moment when you snap your wrist and let go, the Frisbee can be tilted with respect to the ground. We will assume that the moment you throw the Frisbee, it will be pointed in the same direction it is moving — meaning the d1 and v arrows in Figure 2 are perfectly lined up with each other (and the angle of attack, α, is zero). In this project, we will call the frisbee's tilt relative to the ground right when it is thrown the launch angle. Figure 3 below illustrates the launch angle.
 Image Credit: Ben Finio, Science Buddies / Science Buddies
Image Credit: Ben Finio, Science Buddies / Science BuddiesWhen a frisbee is thrown and the disc is parallel to the ground it is thrown at a launch angle of 0 degrees. A frisbee thrown with the leading lip pointed upwards has a positive launch angle and a frisbee thrown with the leading lip pointed downward has a negative launch angle.
Figure 3. An illustration of a Frisbee's launch angle. In the figure, the Frisbee is being thrown to the right. If the front edge of the Frisbee is tilted up, the launch angle is positive. If the Frisbee is horizontal (parallel to the ground), the launch angle if zero. If the front edge of the Frisbee is tilted down, the launch angle is negative.
As a side note, you have probably noticed that a Frisbee does not travel far if it is thrown without spin. Spinning the Frisbee helps it fly by supplying angular momentum, which keeps the Frisbee stable while it is rotating. The faster the Frisbee spins, the more stable it should be.
How do you think the launch angle will affect a Frisbee's flight? Would you want to use a different launch angle to make a short pass to a nearby friend, than a long pass to someone all the way across a field? In this project, you will test how the launch angle affects the distance of a Frisbee's flight, and use this knowledge to predict the flight of a Frisbee based on its launch angle.
Terms and Concepts
- Aerodynamics
- Forces
- Lift
- Gravity
- Air pressure
- Drag
- Launch angle
- Angular momentum
Questions
- What are the forces acting on a Frisbee in flight?
- Can you think of other devices in which angular momentum is important for them to function?
- How do you think the launch angle of the Frisbee affects the distance of flight?
Bibliography
- The Exploratorium (1997). What effect does the rim of a frisbee have on its flight? Sport! Science. Retrieved February 10, 2006.
- Keller, K. (2004, December). The Physics of Frisbee. University of Florida, Undergraduate Physics Newsletter. Retrieved August 6, 2012.
- Glenn Research Center, NASA. (2023, July 6). Guide to Aerodynamics. Retrieved August 4, 2023.
- Glenn Research Center, NASA (2022, August 16). Equal Transit Theory Interactive. Retrieved August 4,2023.
Materials and Equipment
- Tape measure
- String, chalk, or a hose
- Frisbee
- Optional: Masking tape and marker
- Optional: Helper (for measuring and throwing back the Frisbee)
- Optional: Video camera and a second helper to run it
- Lab notebook
Experimental Procedure
- Do your background research and learn about the forces on the Frisbee in flight.
- Use string, chalk, or a hose to make a center line for aiming your throws. The length of the line will depend on how far you think you can throw a Frisbee, but several meters is a good starting point.
- Practice throwing the Frisbee down the center line a few times so you get used to tossing it.
- If you have not thrown a Frisbee much before, you may want to try practicing it for a little while.
- Tip: A good way to throw a Frisbee is by standing sideways with the Frisbee held in front of you (near your other shoulder), then bringing the Frisbee horizontally across you as you throw it.
- c. Also practice throwing the Frisbee just as hard (with the same amount of effort) each time. If you throw the Frisbee really hard sometimes, but really softly other times, this will affect your results.
- If your tape measure is not as long as your typical Frisbee throw, you can make a longer tape measure using a piece of string. Mark off regular intervals with tape labels and a marker, and you are in business.
- Throw the Frisbee as flat and horizontal as you can, aiming it down the center line. When the Frisbee lands, measure the distance between the launch point and the Frisbee's landing point (where it first hit). You can use a helper to help you collect this data. Record this data in your lab notebook.
- If you have a video camera, you can use it to help you analyze the launch angle of the Frisbee. Set it up near you so that it can record your throw without your body blocking the view. Later you can watch and stop the video at the moment that you release the Frisbee and measure the launch angle of the Frisbee. See the Variations section for suggestions on how to do this in more detail.
- If you do not use a video camera, then you or a helper will have to watch closely and estimate the launch angle for each throw. Here is one method you can try: Hold one arm out horizontally and use the other arm to try to match the launch angle that you saw. You can have a helper use a protractor to measure the angle between your arms.
- If there is wind, note the wind speed and direction in your notebook.
- If you clearly made a mistake on the throw (for example, if the release was way off the center line) then do not include it in your results.
- Repeat step 5 at least nine more times, making a total of at least ten good throws thrown from the horizontal angle.
- Try your best to throw with similar arm motion and speed, and impart a similar spin on the Frisbee each time. You want to have the same release point so that your arm is directed along the center line for each launch.
- For each throw, be sure to measure and record the results.
- Repeat steps 5-6 but try throwing the Frisbee with two different positive and two different negative launch angles (refer to Figures 3 in the Introduction for a reminder about what positive and negative launch angles mean). Make at least ten good throws at each of the four of these launch angles.
- To measure the effect of launch angle on Frisbee flight, you will need to try your best to keep all other aspects of the flight the same, as described in step 6a. The one thing you want to vary is the launch angle.
- For each throw, be sure to measure and record the results.
- When you are done collecting your data, average your results (the distance and direction) for each launch angle.
- Make a graph with flight distance on the y-axis and launch angle on the x-axis.
- Is there a relationship between launch angle and distance?
- Can you explain your results in terms of the aerodynamic forces on the Frisbee?
Ask an Expert
Global Connections
The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UNSDGs) are a blueprint to achieve a better and more sustainable future for all.
Variations
- What happens if you include the complication of wind in the equation? How will the flight of the Frisbee® be affected by throwing into the wind? Across the wind? With the wind? How will launch angle change the flight in each of these conditions?
- Compare Frisbee® flight with flight of an Aerobie (open ring flying disc). What differences do you notice? Can you explain them in terms of aerodynamic forces?
- When you throw the Frisbee at very high launch angles, it may experience stall. Aerodynamic stall occurs when the lift force drops dramatically and the drag force increases. This can be very dangerous when it occurs in airplanes. Can you investigate at what launch angle your Frisbee begins to stall?
- For directions on how to use a video camera and computer program to analyze the launch angle and flight path of a Frisbee, see the Science Buddies project How Far Can You Throw (or Kick) a Ball?.
- Can you analyze the left-to-right drift of the frisbee by measuring the angle between where it lands and your center line? Does the launch angle affect the left to right movement? What about other variables, like the amount of spin on the Frisbee, or whether you tilt the Frisbee left or right when throwing it?
Careers
If you like this project, you might enjoy exploring these related careers:
Related Links
- Science Fair Project Guide
- Other Ideas Like This
- Aerodynamics & Hydrodynamics Project Ideas
- My Favorites










