Log In
Summary
Areas of Science
Difficulty
Time Required
Long (2-4 weeks)
Prerequisites
This project requires access to bacteria and antibiotics in a laboratory setting. A basic knowledge of how to work with bacteria is needed to complete this science fair project. Consult the Microbiology Techniques and Troubleshooting guide for information on how to conduct microbiology experiments.
Material Availability
Specialty items, like bacteria and the media to grow them on, can be ordered from online vendors such as Carolina Biological Supply Company.
Cost
High ($100 - $150)
Safety
Requires adult supervision in a laboratory setting. Use sterile technique. Read the Microorganisms Safety Guide before starting any experiments. SRC approval may be necessary.

*Note:
For this science project you will need to develop your own experimental procedure. Use the information in the summary tab as a starting place. If you would like to discuss your ideas or need help troubleshooting, use the Ask An Expert forum. Our Experts won't do the work for you, but they will make suggestions and offer guidance if you come to them with specific questions.
If you want a Project Idea with full instructions, please pick one without an asterisk (*) at the end of the title.
If you want a Project Idea with full instructions, please pick one without an asterisk (*) at the end of the title.
Abstract
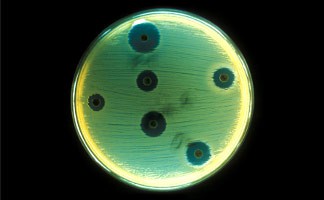
Antibiotics work by destabilizing the metabolism or cellular structure of bacteria, preventing growth, and causing bacteria to die. Some strains of bacteria have mutated and found a way to resist the actions of antibiotics. These are called resistant strains because they resist the actions of available antibiotic treatments. There are many different types of antibiotics that are continually being developed to combat new strains of resistant bacteria. Some antibiotics work better on different bacterial strains than others. Compare the action of different antibiotics on different strains of bacteria. Which type of antibiotic works the best against each strain? Which ones are the most cosmopolitan, and work on the most different strains of bacteria? Can you use genomic techniques and bioinformatics to predict which antibiotics will work best on each bacterial species or strain? (NCBI, 2006; Brown, 2002)Bibliography
- Brown, J. (2002). What the Heck is Antibiotic Resistance?. Retrieved May 1, 2006.
- NCBI, (2006). National Center for Biotechnology Information. Retrieved May 1, 2006.
Ask an Expert
Do you have specific questions about your science project? Our team of volunteer scientists can help. Our Experts won't do the work for you, but they will make suggestions, offer guidance, and help you troubleshoot.
Global Connections
The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UNSDGs) are a blueprint to achieve a better and more sustainable future for all.
This project explores topics key to Good Health and Well-Being: Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages.
Careers
If you like this project, you might enjoy exploring these related careers:
Career Profile
Microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, algae, and fungi) are the most common life-forms on Earth. They help us digest nutrients; make foods like yogurt, bread, and olives; and create antibiotics. Some microbes also cause diseases. Microbiologists study the growth, structure, development, and general characteristics of microorganisms to promote health, industry, and a basic understanding of cellular functions.
Read more
Career Profile
Pharmacists are the medication experts. They advise doctors, nurses, and patients on the correct drug dosage for a patient's weight, age, health, and gender; on interactions between drugs; on side effects; on drug alternatives; on costs; and on ways to give drugs. They also dispense drugs at pharmacies, according to prescriptions, checking for dangerous drug interactions, and educating patients on how to take drugs, what reactions to watch out for, and how long it should take for drugs to work.
Read more
Related Links
- Science Fair Project Guide
- Other Ideas Like This
- Microbiology Project Ideas
- Medical Biotechnology Project Ideas
- My Favorites
Cite This Page
General citation information is provided here. Be sure to check the formatting, including capitalization, for the method you are using and update your citation, as needed.MLA Style
Science Buddies Staff.
"Antibiotic Resistance." Science Buddies,
14 Aug. 2020,
https://www.sciencebuddies.org/science-fair-projects/project-ideas/MicroBio_p021/microbiology/antibiotic-resistance?class=AQVSFF7H6WOAn-yvFgtTOLMwLATXsyCZc0Y8q7WrCfL_Lbr7auB8VWhyxu7HNzMqo_BFEauxH0weLUX0GwRtWdYOjl-TDdvrFkSHr3kuhwWtYg.
Accessed 16 Apr. 2024.
APA Style
Science Buddies Staff.
(2020, August 14).
Antibiotic Resistance.
Retrieved from
https://www.sciencebuddies.org/science-fair-projects/project-ideas/MicroBio_p021/microbiology/antibiotic-resistance?class=AQVSFF7H6WOAn-yvFgtTOLMwLATXsyCZc0Y8q7WrCfL_Lbr7auB8VWhyxu7HNzMqo_BFEauxH0weLUX0GwRtWdYOjl-TDdvrFkSHr3kuhwWtYg
Last edit date: 2020-08-14
Explore Our Science Videos
Paper Rockets - STEM Activity
Paper Bridges STEM Activity
Make a Hygrometer to Measure Humidity – STEM activity