Mammalian Biology Science Projects (18 results)
Do you love furry animals — studying them or even playing with them? Maybe you wonder why your pet loves that certain ball, or shakes hands with one paw more than the other. Or maybe you are curious about how bats navigate through the dark. Then you're sure to enjoy learning about mammalian biology with your pet or other friendly animals you know!
|
Select a resource
Sort by
|
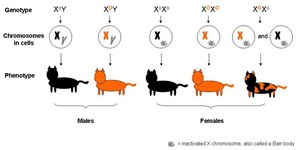
Have you ever seen a tortoiseshell cat? "What kind of cat is that?" you might ask. A tortoiseshell cat has two different fur colors, black or brown and red or orange. The gene that gives rise to the red or orange fur color is on the X chromosome. And did you know that most tortoiseshell cats are female? That's because female cats have two X chromosomes, while males only have one, which allows the females to express two different color combinations! Try this science fair project to figure out…
Read more
Featured
Have you heard that garlic powder is supposed to inhibit the growth of bacteria? Which do you think would make a better disinfectant: a solution of garlic powder or a solution of bleach? This project shows you a straightforward way to compare the effectiveness of different disinfectants (or other antimicrobial agents), by measuring zones of inhibition on a culture plate.
Read more
The great majority of people have a distinct hand preference. How about animals like dogs or cats? Do they show a paw preference? If you like animals, this science fair project might be for you.
Read more
New
Engineers are trying to tackle the world's ocean pollution problem using robots. Some robots, like Mr. Trash Wheel and the ship featured in this Mark Rober video, are stationary and collect trash as it flows out of rivers before it gets into the ocean. Others, like the Jellyfishbot, are mobile and can squeeze into narrower spaces to collect trash:
Can you build and test your own trash-skimming robot? If you do not have access to a natural body of water to test it in, you can use a bathtub or a…
Read more
Have you ever wondered what goes on in your dog's mind? Even though humans have the benefit of language, trying to understand another person's thoughts can be hard enough sometimes. Your dog can't talk, so how can you find out what its brain is capable of? The obvious answer is to study its behavior. This project will show you some behavioral tests you can use to measure canine I.Q.
Read more
Got a pampered pooch in your household? Then you know how much most dogs love their toys. And not just any toy. It has to be that particular beat up ball, gnawed frisbee, or ratty not-so-plush-anymore bunny with only one eye and partial ear remaining. Seems that dogs, like people, have definite preferences for their play things. This fun project investigates what makes a toy interesting to a dog. In these experiments, you and your dog can have some fun while you learn about canine behavior…
Read more
Everyone thinks their dog's the best, but in the case of smelling ability, all dogs possess super powers. In fact, a dog's nose can be over a 1,000 times more sensitive than a human's! In this project, learn about smell from a dog's unique perspective. There will be a whole lot of sniffing going on when you set up these fun experiments to find out what scents your dog and other canine friends find most interesting or appealing.
Read more
New
Artificial intelligence (AI) programs can now generate photorealistic pictures of people who do not exist in the real world. How can you tell if a picture is of a real person or a fake, AI-generated person? What features of the picture do people use to decide whether the face is real or AI-generated? In this project, you will explore these questions as you ask volunteers to look at both real and AI-generated pictures of human faces.
Read more
Did you know that there are over 58 million overweight cats and dogs in the United States? Is your pet one of them? How about your neighbor's cat or your grandma's dog? In this science project you'll determine what percentage of the pets you know are overweight and how their weights compare to pets' weights throughout the United States.
Read more
What is the first thing you do when you wake up on a cold, frosty morning? Snuggle down deeper under the covers? Animals, like puppies and piglets, do not like being cold either, but they do not have hands or blankets to wrap themselves up. So when animals get chilled, they change their behavior and do things like huddle—they curl up close to other animals. In this mammalian biology science fair project, you will see just how much huddling can help reduce heat loss.
Read more
Do you have bats in your neighborhood? Have you heard them "whoosh" by you, but not been able to see them? In this science fair project, you will be able to detect flying bats by listening in on the ultrasonic signals they produce to locate objects in their environment. The bat detector is a useful and fun tool for studying the biology of this nocturnal flying mammal.
Read more
Has your dog ever barked, seemingly for no reason at all? Or has your cat ever stopped and carefully smelled a spot that looked perfectly clean to you? Pets, like people, have senses that they use to learn about and to react to their world, but their senses can be stronger or weaker than people's. In this mammalian biology science fair project, you'll study your pet's sense of taste by conducting taste tests and watching how your pet acts to determine his or her favorite type, flavor, or brand…
Read more
Cats are great house pets, but as every cat observer knows, they are also instinctive hunters. This experiment provides an interesting way to learn about cat behavior. You'll play bird call recordings for pet cats, and watch to see if the cat pays attention to the sound (by turning towards it) or ignores it. Will a pet cat distinguish between the calls of local birds vs. non-local birds?
Read more
|
Explore Our Science Videos
Build a Mini Rain Garden
Volleyball Machine: 2019 Engineering Challenge
Can you solve this air pressure puzzle?