High School, Biotechnology Lesson Plans (6 results)
Yogurt, biofuel, biodegradable plastics, and antibiotics are all examples of products based on biotechnology research and manufacturing techniques. What else will we be able to create as we use biotechnology in new ways?
|
Select a resource
Sort by
|
Lesson Plan
Grade: 6th-12th
5 reviews
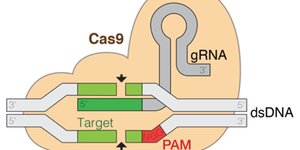
In this lesson plan, students will take a closer look at the most recent developments in gene editing. Specifically, they will learn about the CRISPR technology using various interactive simulations and other resources. Based on their gained knowledge, students will create a model of the CRISPR-Cas9 components and create a stop-motion animation video of the molecular mechanism of CRISPR-Cas9.
Remote learning adaptation:
This lesson plan can be conducted remotely. Students can work…
Read more
NGSS Performance Expectations:
Featured
Lesson Plan
Grade: 6th-8th
7 reviews
Junkbots are easy-to-build robots that you can make using a simple circuit and some recyclable materials. In this lesson, your students will learn about engineering design as they compete to build the fastest robot. No previous robotics experience is required!
Read more
NGSS Performance Expectations:
Lesson Plan
Grade: 9th-12th
2 reviews
This lesson introduces students to the relationships between chromosomes, genes, and DNA molecules. Using the example of a strawberry, it also provides activities that clearly show how changes in the DNA of an organism, either naturally or artificially, can cause changes.
Read more
NGSS Performance Expectations:
New
Lesson Plan
Grade: 6th-12th
Create a two-part system for filtering greywater. Teams will focus on communication and systems engineering as they build separate components to filter solid and liquid waste and then combine them into one device.
Learning Objectives
Students will:
Consider the potential effects of drought and how greywater could be part of the solution.
Design a system for filtering out solid waste or liquid waste.
Consider effective communication strategies with their team.
Collaborate on their design…
Read more
Lesson Plan
Grade: 9th-12th
Students will compare and contrast methods of selective plant breeding, describe the scientific process of creating a genetically modified plant, compare genetically modified soybean seeds to conventional soybean seeds, describe the impact weeds have on plant growth, and understand how a genetically modified seed can help farmers manage weeds.
Read more
NGSS Performance Expectations:
Lesson Plan
Grade: 9th-12th
Students act as if they are biological engineers following the steps of the engineering design process to design and create protein models to replace the defective proteins in a child's body. Jumping off from a basic understanding of DNA and its transcription and translation processes, students learn about the many different proteins types and what happens if protein mutations occur. Then they focus on structural, transport and defense proteins during three challenges…
Read more
NGSS Performance Expectations:
Lesson Plan
Grade: 9th-12th
3 reviews
This lesson compares and contrasts prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and examines the form and function of the plasmid found in prokaryotic cells. Students will then use these principles to simulate how a desirable gene can be isolated and inserted into a plasmid as one step in the process of creating a genetically modified organism (GMO).
Read more
NGSS Performance Expectations:
Lesson Plan
Grade: 9th-12th
Students construct paper recombinant plasmids to simulate the methods genetic engineers use to create modified bacteria. They learn what role enzymes, DNA and genes play in the modification of organisms. For the particular model they work on, they isolate a mammal insulin gene and combine it with a bacteria's gene sequence (plasmid DNA) for production of the protein insulin.Engineering Connection
Bacteria are the most common organisms modified by genetic engineers due to…
Read more
NGSS Performance Expectations:
|
Explore Our Science Videos
Build A Vortex Cannon!
Storm Surge Activity - Protect Houses From Waves
Rubber Band Paddle Boat with Cardboard and Duct Tape